Tax Savings through Section 54 & 54F on Sale of Non-Residential Properties
- November 29, 2023
- Miscellaneous

When selling a non-residential property in India, it is important to understand Section 54 and 54F of Income Tax Act. These provide tax-saving alternatives when selling non-residential assets in India. Individuals can save money on taxes by reinvesting the sale proceeds in residential real estate. People who pay taxes can make smart decisions about buying and selling property and can do tax saving if they know the good parts and rules in these sections. It’s really important for property owners to know the basics of these rules so they can make the most of their investments and still follow the tax laws in India.
| Table of Content |
Overview of Section 54 and 54F of Income Tax Act?
Sections 54 and 54F of India’s Income Tax Act allow tax incentives to persons who sell certain types of assets and reinvest the proceeds in other types of properties. Each section is summarized below:
- Section 54:
-
-
- Section 54 primarily applies to residential properties. When an individual sells a residential property (such as a house or apartment) and makes a profit, they can claim an exemption from paying capital gains tax on that profit if the sale proceeds are reinvested in the purchase of another residential property.
- The key condition is that the new residential property should be purchased within a specified period (usually within one to three years) before or after the sale of the original property.
- The exemption is either partial or complete, depending on the amount reinvested in the new property. If the entire sale proceeds are reinvested, the capital gains tax is fully exempt.
-
- Section 54F:
-
- Section 54F, on the other hand, applies to both residential and non-residential properties. If an individual sells a non-residential property (e.g., commercial property, land, or any other asset), they can claim an exemption from capital gains tax by investing the sale proceeds in a residential property.
- The conditions for Section 54F are similar to Section 54, including the requirement to invest in a residential property within a specified time frame.
- The exemption under Section 54F is also partial or complete, based on the amount reinvested in the new residential property.
Key Benefits of Section 54F
Key Benefits of Section 54F of Income Tax Act in India include:
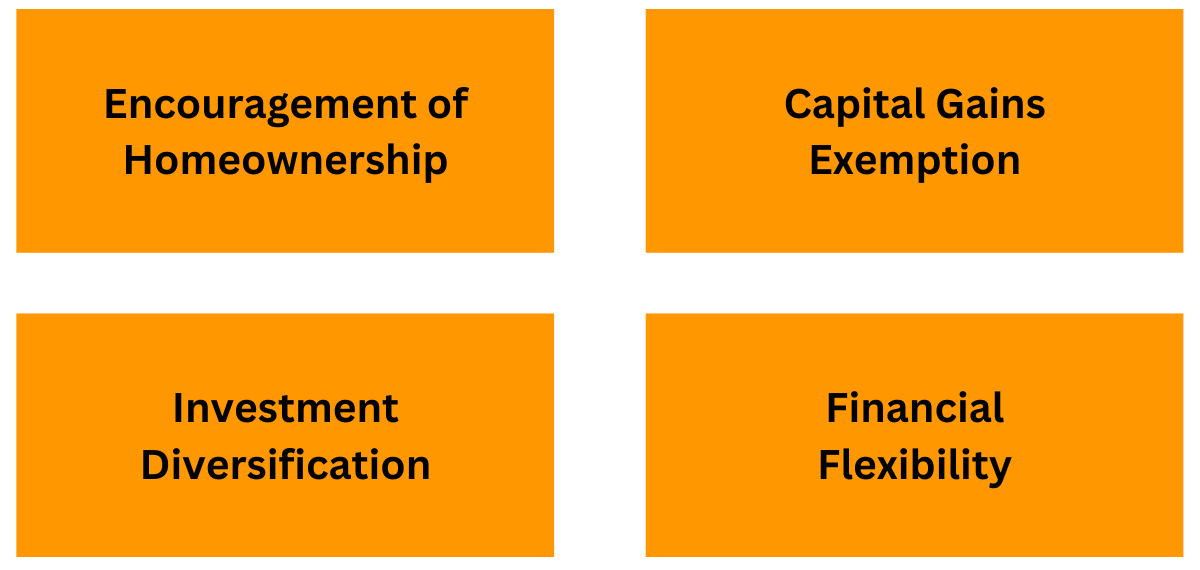
- Encouragement of Homeownership: This rule helps people own homes by encouraging them to invest money from places that are not homes, like offices or stores, into houses where people live. This boosts the real estate area, making it bigger, and makes it easier for more people to find homes.
- Capital Gains Exemption: Section 54F allows persons selling non-residential properties to claim capital gains tax exemptions with the aid of making an investment the proceeds in residential houses, substantially doing tax saving.
- Investment Diversification: This rule helps make investments safer by making it easier to move money from places like offices to homes where people live. This could help balance and mix up the different kinds of investments people have, making them safer.
- Financial Flexibility: Section 54F gives people a break on taxes, which helps them have more money to handle their property deals. This lets them make smarter choices about how they invest and buy properties.
Criteria and Eligibility
Criteria and eligibility for availing benefits under Section 54F of Income Tax Act are as follows:
- Type of Property: The section applies to people or Hindu Undivided families (HUFs) who’ve bought a non-residential property, inclusive of industrial property, business land, or any other asset aside from residential property.
- Reinvestment in Residential Property: The individual ought to utilize the entire net sale attention (the amount received from selling the non-residential belongings) to purchase or assemble a residential property.
- Time Limits: The new residential assets need to be purchased either within one year before or two years after the sale of the non-residential property. as an alternative, the man or woman can assemble a residential belonging inside 3 years from the date of the sale.
- Capital Gains: Other than the new property, the individual cannot own multiple residential house on the date of transfer of the original non-residential asset. Moreover, the capital profits from the sale of the non-residential property ought to be invested within the new residential belongings with a view to qualify for the exemption.
- Important Considerations for Taxpayer
When considering the tax on sale of residential land in India, several important factors can help taxpayers save on capital gains tax. Key considerations include:
- Reinvestment Options: Looking into ways to use Section 54 of the Income Tax Act to delay or reduce the tax you have to pay when selling your house to minimize capital gains tax on the sale of residential property.
- Exemptions and Deductions: Figuring out how selling land affects your money and using the special discounts and money-saving tricks in the Income Tax Act to maybe pay less tax.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to the rules and regulations concerning the tax on the sale of land in India, ensuring proper documentation, and fulfilling reporting requirements to avoid penalties or legal complications.
- Consultation with Tax Experts: Talking to tax experts for tax saving, understanding new tax rules, and planning smartly to pay the least tax possible when selling your house or land.
By considering these factors and staying informed about the latest amendments in the tax laws, taxpayers can make informed decisions and potentially save on capital gains tax when selling residential properties or land in India.
Conclusion
In short, knowing about tax-saving rules like Section 54F in the Income Tax Act is super important for people who want to plan their money well and pay less tax when selling places that aren’t homes. By leveraging the benefits offered under this section, taxpayers can effectively transition their investments from non-residential properties to residential properties while capitalizing on exemptions to reduce their overall tax burden. It’s really important to follow the rules and meet the conditions they set, get help from experts when you need it, and know if there are any changes in tax laws. Doing these things helps you sell property smoothly without problems. When you do this, you can choose wisely and save more on taxes according to the rules in India.
LegalWindow.in is a professional technology driven platform of multidisciplined experts like CA/CS/Lawyers spanning with an aim to provide concrete solution to individuals, start-ups and other business organisation by maximising their growth at an affordable cost. Our team offers expertise solutions in various fields that include Corporate Laws, Direct Taxations, GST Matters, IP Registrations and other Legal Affairs.
Categories
- Agreement Drafting (23)
- Annual Compliance (11)
- Change in Business (36)
- Company Law (148)
- Compliance (90)
- Digital Banking (3)
- Drug License (3)
- FEMA (17)
- Finance Company (42)
- Foreign Taxation (6)
- FSSAI License/Registration (14)
- GST (120)
- Hallmark Registration (1)
- Income Tax (202)
- Latest News (34)
- Miscellaneous (165)
- NBFC Registration (8)
- NGO (14)
- SEBI Registration (6)
- Section 8 Company (7)
- Start and manage a business (21)
- Startup/ Registration (130)
- Trademark Registration/IPR (40)
Recent Posts
About us
LegalWindow.in is a professional technology driven platform of multidisciplined experts like CA/CS/Lawyers spanning with an aim to provide concrete solution to individuals, start-ups and other business organisation by maximising their growth at an affordable cost.