What is Indirect Tax? Understand the Types, Features, and Filing Here
- November 21, 2023
- Income Tax

Are you acquainted with the concept of indirect taxes? Manufacturers purchase the goods and pay taxes in the form of indirect tax. The production, sale, and import of commodities as well as the purchasing of products and services by individuals and commercial entities are charged in the form of indirect tax. Let us discuss the question- What is Indirect Taxes in India?
| Table of Contents |
What is Indirect Tax?
Indirect tax is imposed on an individual when they purchase goods and services. One’s income is not the source of direct collection of indirect tax. The seller when purchasing the goods or services has to pay tax in addition to the real cost. In essence, indirect taxes are levied on behalf of another organization or person. Usually, the manufacturer or supplier bears the burden of these taxes, which they transfer to the customer. Some indirect tax examples are-excise duty, entertainment tax, sales tax, etc.
Also read– Direct and Indirect Taxes: Basics
Features of Indirect Tax
Here are a few features of indirect taxes:
- Avoidance of Evasion: Since taxes are now paid directly through goods and services, it is challenging to evade them.
- Nature: Taxes are inherently regressive, but since the introduction of the GST, they have become more progressive.
- Tax Payment: The seller will provide the government with the taxes, which will then be passed on to the buyer.
- Consumer is not directly affected: The main cause of direct tax evasion is that it is charged directly from income but indirect taxes do not have such a problem because they are not directly affected.
- Revenue for the government: Since this type of tax cannot be easily circumvented and applies to most commodities, it serves as a major source of revenue for the government and contributes higher than the direct tax.
Advantages of Indirect Tax
The advantages of indirect tax are-
- Maintaining the fairness of the tax system is aided by indirect taxes because people who can afford more expensive goods will ultimately pay more in taxes.
- Compared to direct taxes, indirect taxes are generally simpler to pay and collect. Some are applied during the transaction, such as the Goods and Services Tax, at the point of consumption or purchase.
- The objective of indirect taxes is to reduce tax evasion, particularly those that have a multi-stage element like the GST.
- One of the most important functions of indirect taxes is to deter people from using dangerous goods like alcohol and cigarettes. These products are costly so higher tax rates can be applied. Price increases serve as a disincentive and may cause consumption to decline.
Different Types of Indirect Taxes in India
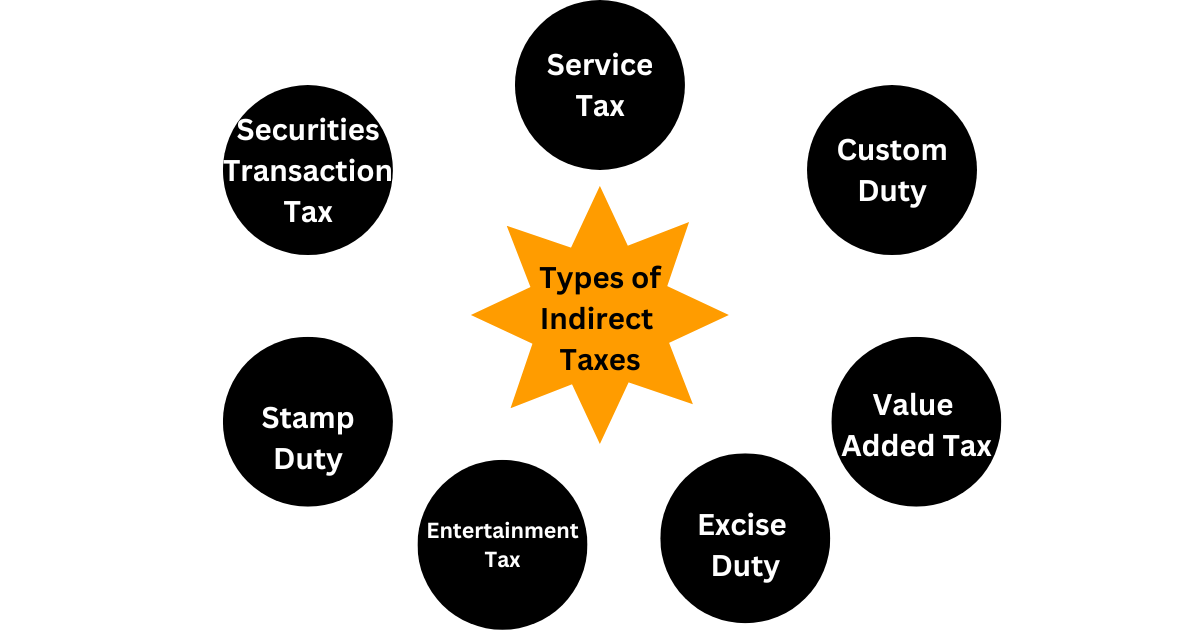
Earlier, various types of indirect taxes were levied as follows:
- Service Tax: It is charged for the services availed by the customer.
- Value Added Tax (VAT): It is paid on the added value of the sale of goods.
- Excise duty: It is paid for the production of goods. For example, if a person manufactures automobiles, he is required to pay excise duty on the manufactured automobiles.
- Stamp duty: It is paid when real estate is sold. Stamp duty is also mandatory for all types of legal documents.
- Entertainment Tax: This tax is levied on every transaction related to entertainment. For example, tickets to cinemas, video game arcades, theatre performances, exhibitions, theme parks and sporting activities.
- Securities transaction tax: Securities transaction tax is levied at the time of trading of securities through the Indian stock exchange.
- Custom Duty: Payable on goods imported from outside India.
Payment and Collection of Indirect Taxes
Each step of the supply chain is subject to indirect taxes, which are collected by the provider and paid by the customer to the government.
The reverse charge system often used in GST requires the customer or recipient of the product to pay tax to the government. Services such as debt collection agents, freight forwarders and insurance agents are alert services that use pass-through procedures. Raw cotton, cashew nuts, used cars and other GST products fall under the reverse charge mechanism.
Takeaway
India is only one of several governments in the world whose budgetary policies heavily rely on indirect taxation. Indirect taxes are considered to be easily enforceable and convenient taxation as they come mostly from the organized sector. Indirect taxes provide a significant portion of the government revenue stream in India and are essential for funding public spending, inspiring the economy, and accomplishing socio-economic objectives.
In case of any query regarding the question- What is Indirect Taxes in India, a team of expert advisors from Legal Window is here to assist you at every step. Feel free to reach us at admin@legalwindow.in.
LegalWindow.in is a professional technology driven platform of multidisciplined experts like CA/CS/Lawyers spanning with an aim to provide concrete solution to individuals, start-ups and other business organisation by maximising their growth at an affordable cost. Our team offers expertise solutions in various fields that include Corporate Laws, Direct Taxations, GST Matters, IP Registrations and other Legal Affairs.
Categories
- Agreement Drafting (23)
- Annual Compliance (11)
- Change in Business (36)
- Company Law (148)
- Compliance (90)
- Digital Banking (3)
- Drug License (3)
- FEMA (17)
- Finance Company (42)
- Foreign Taxation (6)
- FSSAI License/Registration (14)
- GST (118)
- Hallmark Registration (1)
- Income Tax (200)
- Latest News (34)
- Miscellaneous (164)
- NBFC Registration (8)
- NGO (14)
- SEBI Registration (6)
- Section 8 Company (7)
- Start and manage a business (21)
- Startup/ Registration (128)
- Trademark Registration/IPR (40)
Recent Posts
- Post incorporation compliances for companies in India April 30, 2024
- Startup’s Guide to Employee Stock Ownership Plans April 29, 2024
- Master Secretarial Audit: A Complete Compliance Guide April 27, 2024
About us
LegalWindow.in is a professional technology driven platform of multidisciplined experts like CA/CS/Lawyers spanning with an aim to provide concrete solution to individuals, start-ups and other business organisation by maximising their growth at an affordable cost.








