The ITA Act, 1961 includes guidance for calculating the income of individuals by its appropriate provisions. It plays an important role in the calculation of income of individuals. This article deals with a gentle explanation of section 24 of the income tax act and its definition, deduction under Section 24, benefits, eligibility criteria, and typical errors to avoid while claiming deductions.
Contents |
A Look into Section 24 of ITA, 1961
In India, Section 24 of ITA, 1961 gives support to individuals in getting a deduction of interest in their loans. This will only be in interest payment and not in the repayment of the loan. It stood to support individuals who have taken their loans to buy or build homes. Our government allows interest deduction under section 24 of ITA, 1961 to encourage the growth in real estate.
Things to Remember while Implementing Section 24 of ITA, 1961
It is crucial to remember some things while claiming Section 24 of the Income Tax Act, 1961. These help to maximize the benefits provided by Section 24. The following are some important things to remember while implementing Section 24 of ITA, 1961.
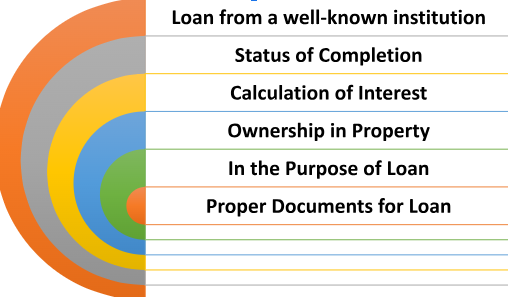
- Loan from a well-known institution: To qualify for Section 24 deductions, the loan must be secured from a recognized institution. It is critical to confirm that the lender is authorized by authorities and follows all applicable rules and regulations. Loans from family members, friends, or unregistered lenders may not be eligible for Section 24 deductions. People can ensure they meet the criteria and get interest deductions on their home loans by taking these elements into account while implementing Section 24 of the ITA.
- Status of Completion: To claim deductions under Section 24, the property’s construction must be finished and possession obtained. This implies that the taxpayer should be able to occupy and use the property.
- Calculation of Interest: Only the interest part of the loan is eligible for the deduction under Section 24, not the repayment. To claim the deduction, you must precisely compute the interest paid over the year. The interest rate, loan amount, and payback schedule should all be considered in the computation. Interest calculation errors or inaccuracies might result in deductions and significant tax issues.
- Ownership in Property: The taxpayer must be the owner of the property used for the loan. It is vital to save proof of ownership, such as property records and registration papers, for verification purposes.
- In the Purpose of Loan: For example, to qualify for a housing loan interest deduction under section 24, the loan funds must be used exclusively for this particular thing itself. Using the loan for expenses or investments may result in the loan being ineligible for deductions. After all, the financing must be secured to purchase, build, repair, or renovate a property.
- Proper Documents for Loan: Proper documentation for the house loan is essential. Loan agreements, payback plans, interest certificates, and receipts are all part of this. These records serve as verification of the loan, interest paid, and other pertinent information. Documentation is essential for supporting Section 24 claims as well as future tax assessments or audits.
It is recommended that taxpayers speak with a tax specialist or seek counsel to understand the specifics of Section 24 based on their situation.
Individuals can ensure compliance with rules by paying attention to these facts while implementing Section 24 of the Income Tax Act, 1961, and can take advantage of their rights under this section. Deductions may not be allowed if the construction is still in process or if ownership of the property has not been taken until the completion and possession conditions are met.
Also read: Tax benefit on Home Loan under Income Tax Act, 1961
Deductions Categorised under Section 24 of ITA, 1961
Deductions are available under Section 24 of the Income Tax Act for the following categories:
- Salaried Employees: Salaried employees are also entitled to claim deductions for home loan interest. However, for homeowners, the maximum deduction allowed is Rs. 2 lakh per year, regardless of the amount of interest paid.
- Homeowners (other than self-employed): Individuals or homeowners who are not self-employed get a deduction in the payment of interest regarding their loans. The maximum deduction allowed is Rs. 2 lakh per year. It is critical to note that the loan must be used to acquire, build, repair, or renovate a property, and the property must be owned and occupied by you as the taxpayer. The housing loan interest deduction under section 24 is a perfect example that comes under this category.
- Self-employed individuals: If you are self-employed, you can deduct the interest on your house loan as a business cost. However, keep in mind that the loan should be utilized to acquire, build, repair, or renovate a property used for your business or profession.
This ensures that you have access to personalized information about Section 24 deductions.
Benefits Under Section 24 of ITA
Section 24 of the Income Tax Act provides taxpayers with several benefits to lessen their tax burden and promote homeownership. The following list of advantages that people may use under Section 24 is detailed:

- Reduced Taxable Income: One of the benefits provided by Section 24 is a reduction in income. The interest paid for a home loan can be considered an expense. Thus, it can be used as a tax deduction. If the taxable income is lowered in reason of the deducted interest amount it results in less tax liability for an individual or the taxpayer.
- Maintaining Consistency in EMI Outflow: Home loans typically consist of EMIs that comprise both the principal and interest sections. Section 24 provides a deduction that alleviates the tax burden thereby adding to the stability of EMI payments. This deduction substantially reduces people’s tax liability, giving them more disposable money to manage their loan repayments effectively.
- Economical Relief: For those who have taken out a house loan, the interest-paid deduction provides much-needed relief. Interest responsibilities are common with home loans, and the provision stated in Section 24 helps to ease this load. With loan amounts and prolonged payback periods, the resulting tax savings can be fairly large for people.
- Encouragement for Home Ownership: Section 24 is quite important in terms of encouraging homeownership in India. Its goal is to provide deductions on the interest portion of home loans as an incentive for people to consider investing in real estate. The government’s goal in launching this initiative is to stimulate the real estate sector, thereby promoting growth.
- Attaining Long-Term Savings: Taking advantage of Section 24’s benefits can result in long-term savings. Individuals might enjoy cheaper tax payments throughout their loan by reducing their income. These collected savings can develop significantly over time, providing individuals with flexibility for numerous efforts such as investments, retirement planning, or satisfying other essential monetary goals.
Eligibility Requirements Under Section 24 of ITA, 1961
Individuals must meet the requirements outlined in Section 24 of the Income Tax Act to be required:
- A loan from a Well-known Organization: The loan needs to come from a company that the appropriate authorities have acknowledged. Maintaining the loan’s documentation is also vital.
- Property Construction Should be Complete: It’s critical that the property’s construction is finished and that the owner has taken control of it.
- The Function/Purpose of Loan: The goal of the loan is to buy, build, fix up, or renovate a piece of real estate.
Also, read: Concept of Housing Loans & EMI’s Business in India
Typical Errors to Prevent
The following common errors should be avoided by people when claiming deductions under Section 24 of the ITA, 1961:
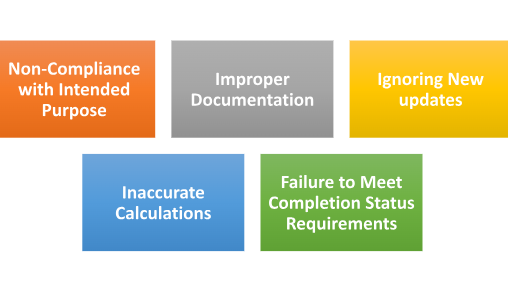
- Non-Compliance with Intended Purpose: The loan must only be used for buying, building, fixing up, or renovating real estate. Any use of the loan for investments or costs could potentially prevent deductions from being claimed.
- Improper Documentation: To properly substantiate deduction claims, documentation is essential. When seeking to verify deductions during tax assessments, failing to retain records such as loan agreements, payback schedules, interest certificates, and receipts may present challenges.
- Ignoring New updates: Any changes to the tax legislation relating to Section 24 must be kept in mind. Staying out of current might lead to calculations going wrong or violation of the most recent regulations.
- Inaccurate Calculations: When calculating the interest component to be deducted, calculations must be accurate. Failure to compute the interest amount can result in claims that could either under or over-report deductions.
- Failure to Meet Completion Status Requirements: To qualify for any deductions, the property must be finished and in possession. If these requirements are not met, deductions may be suspended until the property is accepted as fit for habitation.
Closing Remark
In India, taxpayers can claim deductions for the interest they pay on loans under Section 24 of the Income Tax Act. This is a great opportunity for them. The provision helps in encouraging property ownership and handling people’s tax obligations. Thus, taxpayers can maximize their benefits by the understanding definition, possible deductions, benefits, etc. within Section 24.
In case of any query regarding Section 24 of the Income Tax Act, 1961, feel free to connect with our legal experts at Legal Window at 72407-51000.
CA Pulkit Goyal, is a fellow member of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) having 10 years of experience in the profession of Chartered Accountancy and thorough understanding of the corporate as well as non-corporate entities taxation system. His core area of practice is foreign company taxation which has given him an edge in analytical thinking & executing assignments with a unique perspective. He has worked as a consultant with professionally managed corporates. He has experience of writing in different areas and keep at pace with the latest changes and analyze the different implications of various provisions of the act.
Categories
- Agreement Drafting (23)
- Annual Compliance (11)
- Change in Business (36)
- Company Law (148)
- Compliance (90)
- Digital Banking (3)
- Drug License (3)
- FEMA (17)
- Finance Company (42)
- Foreign Taxation (6)
- FSSAI License/Registration (14)
- GST (118)
- Hallmark Registration (1)
- Income Tax (200)
- Latest News (34)
- Miscellaneous (164)
- NBFC Registration (8)
- NGO (14)
- SEBI Registration (6)
- Section 8 Company (7)
- Start and manage a business (21)
- Startup/ Registration (130)
- Trademark Registration/IPR (40)
Recent Posts
- NGO Darpan Registration in Jaipur May 2, 2024
- Registration of Charges with ROC May 1, 2024
- Post incorporation compliances for companies in India April 30, 2024
About us
LegalWindow.in is a professional technology driven platform of multidisciplined experts like CA/CS/Lawyers spanning with an aim to provide concrete solution to individuals, start-ups and other business organisation by maximising their growth at an affordable cost.









