Is Directorship under Private Limited Company a status or responsibility?
- June 4, 2021
- Company Law
| Table of contents: |
Introduction:
In today’s era, Private Limited Company is one of the most common and popular form of business organisation which is governed under the Companies Act, 2013. Under a company, the day to day activities are carried by the Board of Directors. Board of Directors are the key managerial persons of the company i.e. they are the governing body of company.
Board of directors are those persons that are elected by the shareholders of company to handle the affairs of the Company and these are the representatives of the Company and the shareholders. These persons are directly accountable to the investors, creditors, etc and provide a report to investors on company’s strategies, future plan and growth. As a board of director, one should keep various things in mind, roles and responsibilities should be the first task when appointed.
Seeing today’s scenario, Companies Act, 2013 also increased the responsibilities of Directors like reporting compliances and penalties.
Requirement to become a Director in a Company
As per the Companies Act, 2013 only an individual can be appointed as a Director. This means that any corporate body, association, firm, etc cannot be appointed as Director. A person shall not consider for appointment as a Director in following cases:
- person of unsound mind
- undischarged insolvent
- an insolvent
- person convicted by a court of any offence (imprisoned for at least six months and five years has not elapsed)
- person disqualified for appointment as a director
- He has not paid any calls in respect of any shares of the company held by him
- person convicted of the offence dealing with related party transactions in preceding five years
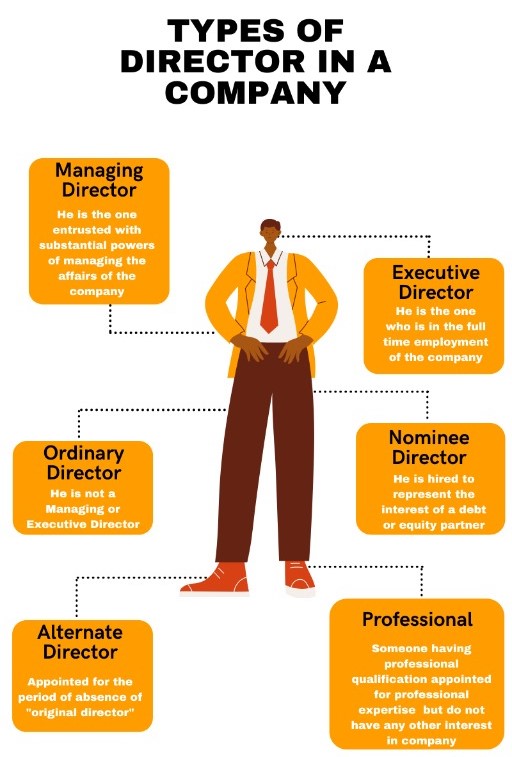
What are the provisions of appointment and cessation of directors?
- Appointment: As per the provisions of Companies Act, 2013 Directors are generally appointed by the members of the company and sometimes may also be appointed in Board meeting. After appointment of Director, intimation in Form DIR- 12 must be given to ROC within 30 days of appointment.
- Cessation: The director’s office can be vacated in various situations such as disqualification, resignation, death, removal, etc. In case of cessation, intimation in Form DIR-11 must be given to ROC within 30 days of cessation.

What are the Duties and Responsibilities of Directors?
As per the Companies Act, 2013 directors have a lot of duties and responsibilities and non- compliance of which attract penalties, disqualification or even imprisonment. The various responsibilities of directors are as follows:
- Maintenance of Books of Accounts: As per the Companies Act, 2013 every company is required to maintain books of accounts and other relevant books and papers on accrual basis for every financial year. Such books of accounts and other relevant books and papers are generally kept at registered office. However, such books of accounts and other relevant books and papers can be kept at any other place in India with the approval of Board of Directors and intimation must be given to ROC for same within seven days of such decision.
- Board Meetings: According to Companies Act, 2013 board meetings must be held at least 4 times in each calendar year with a maximum gap of 120 days between two meetings. This is the responsibility of directors to conduct board meetings on a regular basis. The board meeting shall consist of quorum of at least two directors or one-third of the total number of directors, whichever is higher. Board meeting can be held at any place or at any time, the notice of the same should be given to each director at least seven days before the date of meeting.
The discussions of the meeting required to be written and recorded in the form of “Minutes of Board Meeting” and maintained at the Registered Office of the Company. - Shareholders Meetings: As per the provisions of Companies Act, 2013 every company is required to conduct AGM once in every financial year and an EGM can be called whenever is required but only on a working day with in normal business hours (9 am to 6 pm).
AGM must be conducted within a period of 6 months (with a maximum gap of 15 months between two such meetings) from the date of closing of the financial year. Notice intimating the date, time and venue of the meeting must be given at least 21 clear days in advance of the Meeting. Two members personally present will be the quorum of the meeting. - Company filings: It is the duty of directors of company to file certain information with ROC in prescribed forms and within the time limits of the Act.
Companies are required to file Financial Statements, Director’s Report, Auditors Report and other documents with ROC within 30 days of date of AGM. Companies also required filing Annual Return within 60 days of date of AGM to ROC as well as to intimate the Registrar of Companies as and when any event takes place in the Company.
- Financial Statement and Statutory Audit
Financial Statement includes the following:- Balance sheet
- Profit & Loss A/c
- Cash Flow Statement
- Notes to A/c’s
- Statement of changes in other equity
It is the duty of directors to maintain financial statements to provide true and fair view of the Company and make sure that these statements are audited by the statutory auditor appointed by the company in this regard. The statutory auditor must check whether the company is providing a fair and accurate representation of its financial position. These financial statements are approved by board and signed by directors.
- Statutory Registers and Records: Company should maintain numerous statutory registers and records as needed by the Companies Act like Register of Shares, Members, Directors & Key Managerial Personnel, Debenture holders, Contracts with related parties etc.
Other than incorporation documents of the company, resolutions of the AGM, EGM, Board Meetings, minutes of the meetings etc are needed to be preserved by the Company for such period as needed by the Companies Act, 2013. - Disclosure by Directors: As per the Companies Act, 2013, every director is required to intimate that he is not disqualified in Form DIR-8 and have to disclose its interest in other companies, bodies corporate, firms, association of Individuals every year.
- Displaying Company’s Identity: Directors should make sure that name, address of registered workplace and corporate identity number (CIN) along with telephone number, fax number, e-mail and website addresses, if any, are written in all its business letters, bill heads, letters, papers and in all its notices and different official publications.
The Company’s name and address must be displayed outside of every office or place during which business is carried on. - Charges: The Directors required to ensure that particulars of any charge created or attached to the property acquired by the corporate are intimated to ROC within 30 days of such creation or acquisition of property in prescribed form and register of charges for the same will also be maintained at ROC.
- Other Statutory Duties: The directors of companies are also required to follow other laws and acts like Income Tax Act, 1961, labour laws, etc.
Conclusion
Along these lines, Companies Act, 2013 is absolutely an extremely creative and milestone enactment in regard of the obligations and duties of the executives of organizations moreover. Both general classes of chiefs, to be specific, the executives having financial association with the organization, and the free chiefs, have been appropriately thought to be under this develop enactment for executives. It looks to make the corporate administration and administration in India rather effective, completely responsible, straightforward, and maximally gainful to all partners and related experts, through this insightful enactment over obligations and duties of chiefs in Indian organizations.
LegalWindow.in is a professional technology driven platform of multidisciplined experts like CA/CS/Lawyers spanning with an aim to provide concrete solution to individuals, start-ups and other business organisation by maximising their growth at an affordable cost. Our team offers expertise solutions in various fields that include Corporate Laws, Direct Taxations, GST Matters, IP Registrations and other Legal Affairs.
Categories
- Agreement Drafting (23)
- Annual Compliance (11)
- Change in Business (36)
- Company Law (147)
- Compliance (88)
- Digital Banking (3)
- Drug License (3)
- FEMA (17)
- Finance Company (42)
- Foreign Taxation (6)
- FSSAI License/Registration (14)
- GST (116)
- Hallmark Registration (1)
- Income Tax (199)
- Latest News (34)
- Miscellaneous (164)
- NBFC Registration (8)
- NGO (14)
- SEBI Registration (6)
- Section 8 Company (7)
- Start and manage a business (20)
- Startup/ Registration (126)
- Trademark Registration/IPR (40)
Recent Posts
About us
LegalWindow.in is a professional technology driven platform of multidisciplined experts like CA/CS/Lawyers spanning with an aim to provide concrete solution to individuals, start-ups and other business organisation by maximising their growth at an affordable cost.







