
GST (Goods and Service Tax) is a tax regime that is encouraged by the Government to promote an integrated business based in India. It allows every inspector to self-assess his or her tax liability and submit timely refunds to the government without the substantial intervention of any tax official. As the state places greater emphasis on self-assessment processes, it imposes a strict audit approach, which will ensure effective measurement and compliance with all legal provisions by every taxpayer. This blog highlights all you need to know about GST Audit.
Quick summary of GST Audit
GST Audit operates annually on those registered GST (GSTIN) businesses with a profit of more than Rs.2 crore, on sales of goods or services during the financial year. It is dealt with under Section 35 (5) and 44 (2) of the CGST Act.
In terms of the Finance Act, 2021, the need for GST testing and GSTR-9C submission as accepted by the CA/CMA is withdrawn. It will take effect once notified by CBIC. Meanwhile, according to the 43rd GST Council meeting held on 28 May 2021, the GST Council recommended that GSTR-9C could be submitted as a guarantee by taxpayers with a combined annual profit of or more than Rs.5 million. The same is announced by the CBIC on 11 June 2021.
GST Audit and its Requirement
Audit under the GST revolves around records inquiry, returns, and other documents maintained by a GST registered person (registrant). It also verifies the validity of the declared interest, payable taxes, required refunds, and the input tax credit available and evaluates other such compliance under the GST Act to assess an authorized professional.
GST is a trust-based tax administration in which the taxpayer is required to self-assess his or her tax debt, pay taxes, and file refunds. Therefore, to ensure that the taxpayer properly assesses his or her tax liability a rigorous research method is required. Various steps are being taken by the government to make better use of the GST and auditing is one of them.
Kinds of GST Audit
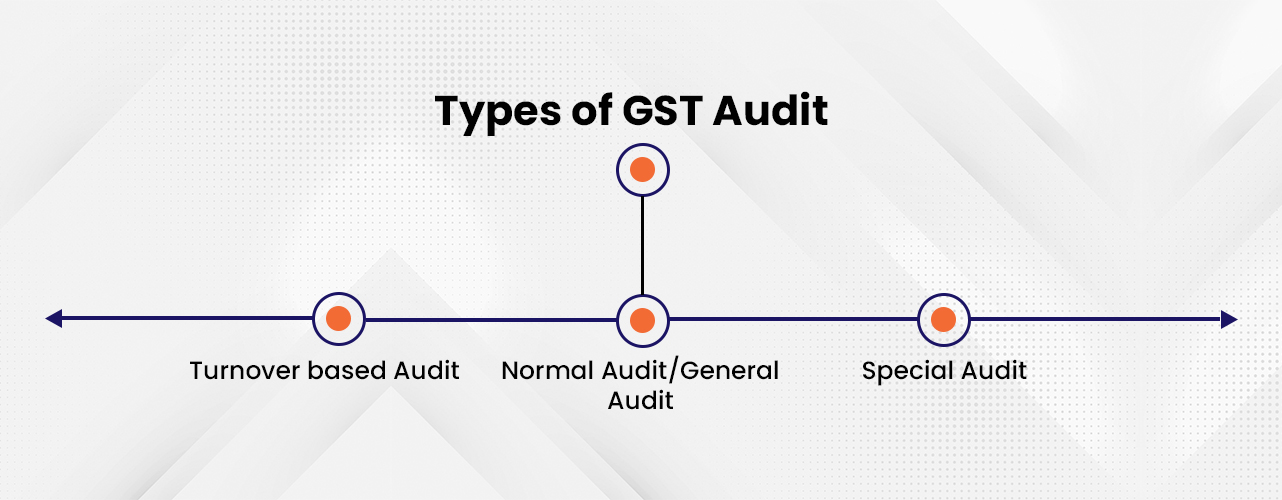
- Turnover-based Audit– In this type of audit every registered person whose profit for the entire financial year exceeds 2 Crore must compulsory provided a copy of the audit records and conciliation statement and FORM GSTR-9C attested and certified by a Chartered Accountant or Cost Accountant to the tax department.
- Normal Audit– As a general audit, the Commissioner, legal representative, and any other authorized official may conduct an audit of any registered person for a period and in the prescribed manner.
- Special Audit-The registered person may be instructed at any time to have his or her records checked by a Chartered accountant or Cost accountant during the investigation, examination, inquiry, or any other proceedings depending on the severity of the case.
GST Audit- Timeline and Applicability
The Central Goods and Services Tax law provides for a clear provision under Section 35 (5) according to which GST Audit applies to every taxpayer whose income during the financial year exceeds INR 2 Crore and you will find that his or her accounts have been audited by a chartered accountant or cost accountant on or before 31st December, after the end of the financial year.
Under the GST audit, the taxpayer is required to submit an electronic receipt each year and a copy of the audited annual account and a reconciliation statement incorporating the amounts stated in the revised financial statements and the audited annual financial statements.
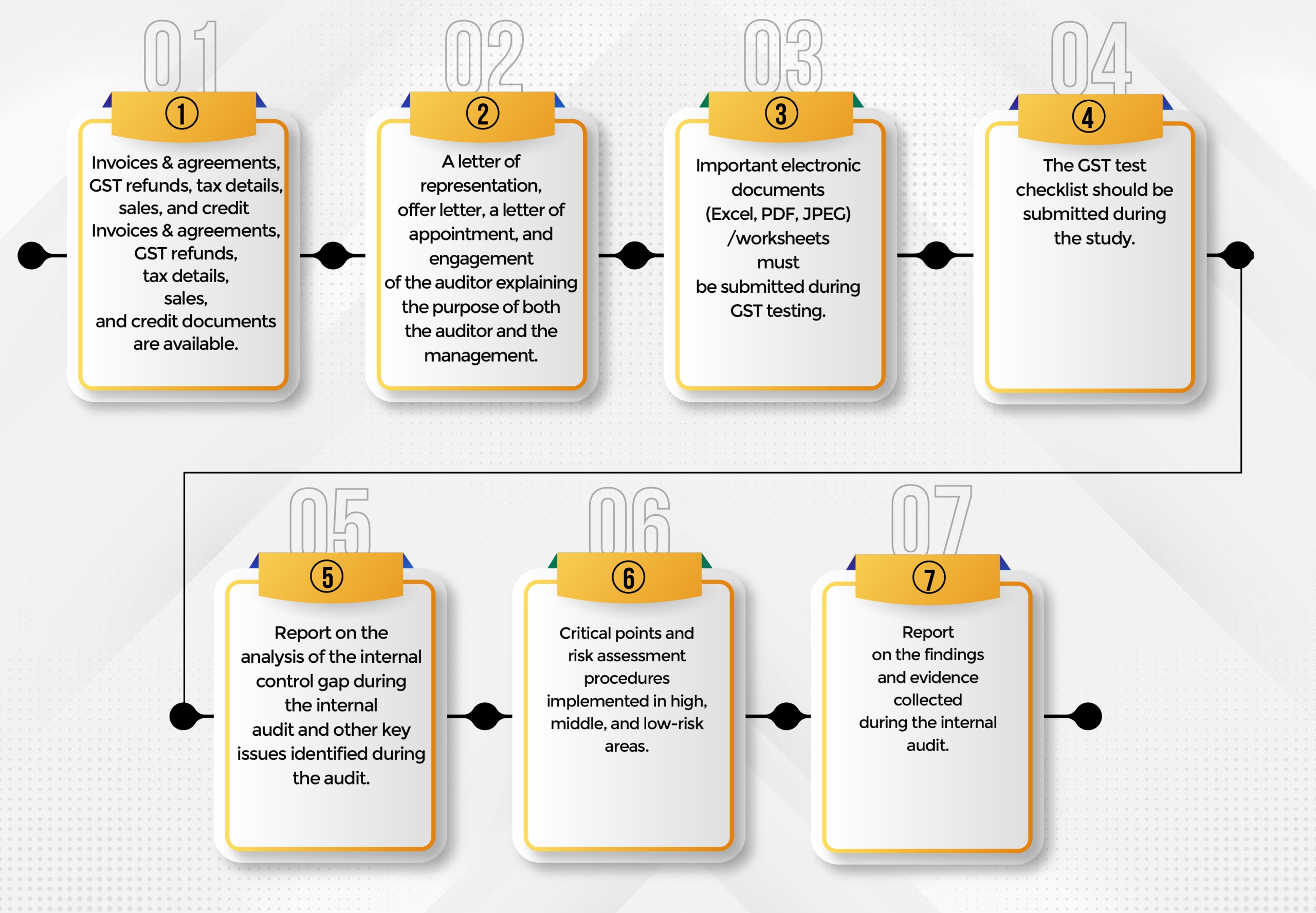
Documents required
Managers must submit the following documents, reports, and invoices in the event of a GST Audit:
Forms to be filled for GST Audit
A taxpayer must complete Form GSTR-9C, which is divided into two parts: Part A and Part B.
Part A is a reconciliation statement that is divided into five sections:
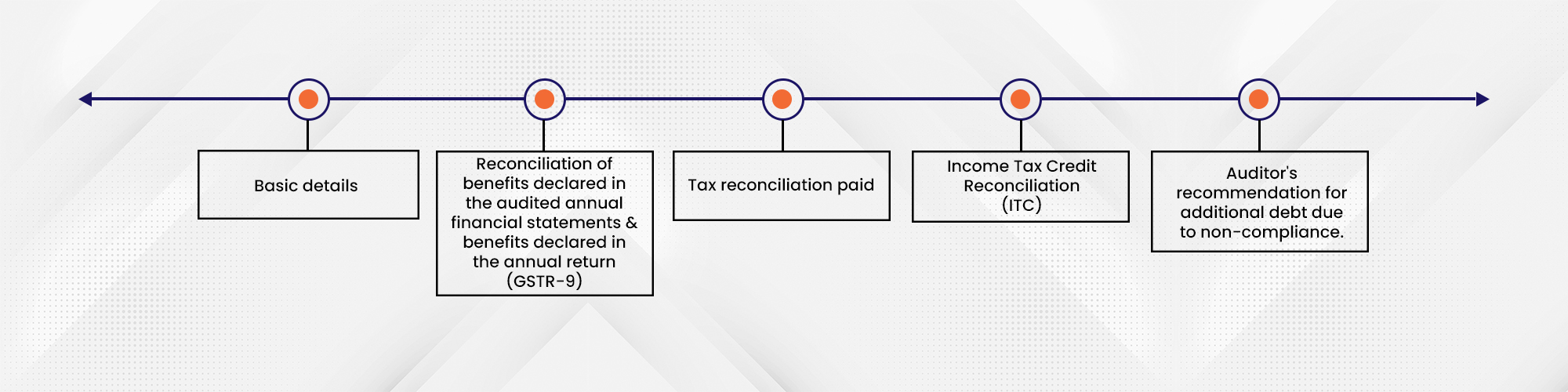
Part B is a certificate issued by the auditor confirming the validity of the information in Part A and the details as submitted in the annual review.
GSTR-9C can be approved under two conditions; one is when a reconciliation statement is drawn up by someone other than the auditor and the other is when a reconciliation statement is issued by the auditor. The certificate report format will vary depending on who the certificate is.
Auditor’s Qualification for GST and Eligibility
Only a Chartered Accountant or Cost Accountant can do GST Audit under Section 35.
Note that-
- The Internal Auditor may not be appointed in the same manner as the GST Auditor.
- GST law does not allow a GST employee to conduct the audit. Audit authority is granted only to a Chartered Accountant or Cost Accountant who is an active or employed employee of a Chartered Accountants or Cost Accountants firm. Therefore, a Chartered Accountant should not be registered as a GST employee to issue an Audit Report.
- Where an organization or company has multiple branches registered under the GST in the various states/UTs, the total benefit of all such branches is taken into account when calculating the limit of Rs. 2 crores.
Audit by Tax Authorities
The authorized officer and his or her designee will conduct an audit of the registrant’s books and accounts, verify all required documents, and i.e. verify the records kept by the registrant and the returns and statements provided under the act. The appropriate authority and its team shall verify the profitability of the tax, the tax rate applied to the provision of goods or services or both, the exemptions and deductions demanded, the required refunds, the applicable and applied tax credit credits, and record the findings in the audit reports.
- A 15-day notice is required for conducting the audit.
- Completion of the audit will be within 3 months from the date the audit is started.
- The CGST / SGST Commissioner may extend the above time limit by another six months.
Responsibilities of an Auditee
- Provide the information required by tax authorities that may be required for further audit purposes, and
- Provide a place for verification of accounts/records required or available by tax authorities, and
- Provide completion assistance during the audit.
The authorized officer may notify the person of his/her audited records of any reported conflict if any, and the said registrant may submit his/her response, and the relevant authority will finalize the audit findings after considering the response provided.
Completion of the Audit
- The relevant officer will complete the audit after considering the registrant’s reply to the audit observations brought to his or her notice during the audit.
- The authorized official within 30 days from the end of the audit will inform the registrant of his or her findings, reasons for the findings, and his or her rights and responsibilities.
- If the audit results in the receipt of any unpaid/temporarily paid or refundable amount or incorrect tax credit, initiation and recovery process will be instituted.
Final words
To familiarize auditors with the information to be reported in the report and the areas to be audited under the audit, the department has provided a copy of the various offline forms for GST auditing and annual returns. The audit report takes on added significance as it will be useful for references down the line. All you need to know about GST Audit has been covered to provide it a clearer picture and familiarize the auditee.
CA Pulkit Goyal, is a fellow member of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) having 10 years of experience in the profession of Chartered Accountancy and thorough understanding of the corporate as well as non-corporate entities taxation system. His core area of practice is foreign company taxation which has given him an edge in analytical thinking & executing assignments with a unique perspective. He has worked as a consultant with professionally managed corporates. He has experience of writing in different areas and keep at pace with the latest changes and analyze the different implications of various provisions of the act.
Categories
- Agreement Drafting (23)
- Annual Compliance (11)
- Change in Business (36)
- Company Law (146)
- Compliance (88)
- Digital Banking (3)
- Drug License (3)
- FEMA (17)
- Finance Company (42)
- Foreign Taxation (6)
- FSSAI License/Registration (14)
- GST (115)
- Hallmark Registration (1)
- Income Tax (199)
- Latest News (34)
- Miscellaneous (164)
- NBFC Registration (8)
- NGO (14)
- SEBI Registration (6)
- Section 8 Company (7)
- Start and manage a business (20)
- Startup/ Registration (126)
- Trademark Registration/IPR (40)
Recent Posts
- Guidelines of GST on Hotel, Restaurant & Outdoor Catering Services April 16, 2024
- Copyright Law and Artificial Intelligence April 16, 2024
- Understanding Trademark Objection under Section 11 April 15, 2024
About us
LegalWindow.in is a professional technology driven platform of multidisciplined experts like CA/CS/Lawyers spanning with an aim to provide concrete solution to individuals, start-ups and other business organisation by maximising their growth at an affordable cost.









